Dental health and aesthetics are increasingly becoming a focal point of modern dentistry, and Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) crowns play a significant role in this field. PFMs have been a popular choice for decades, offering a blend of strength and aesthetic appeal. In this post, we’ll explore what PFMs are, their benefits, considerations, and advancements in this technology.
What Are Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal Crowns?
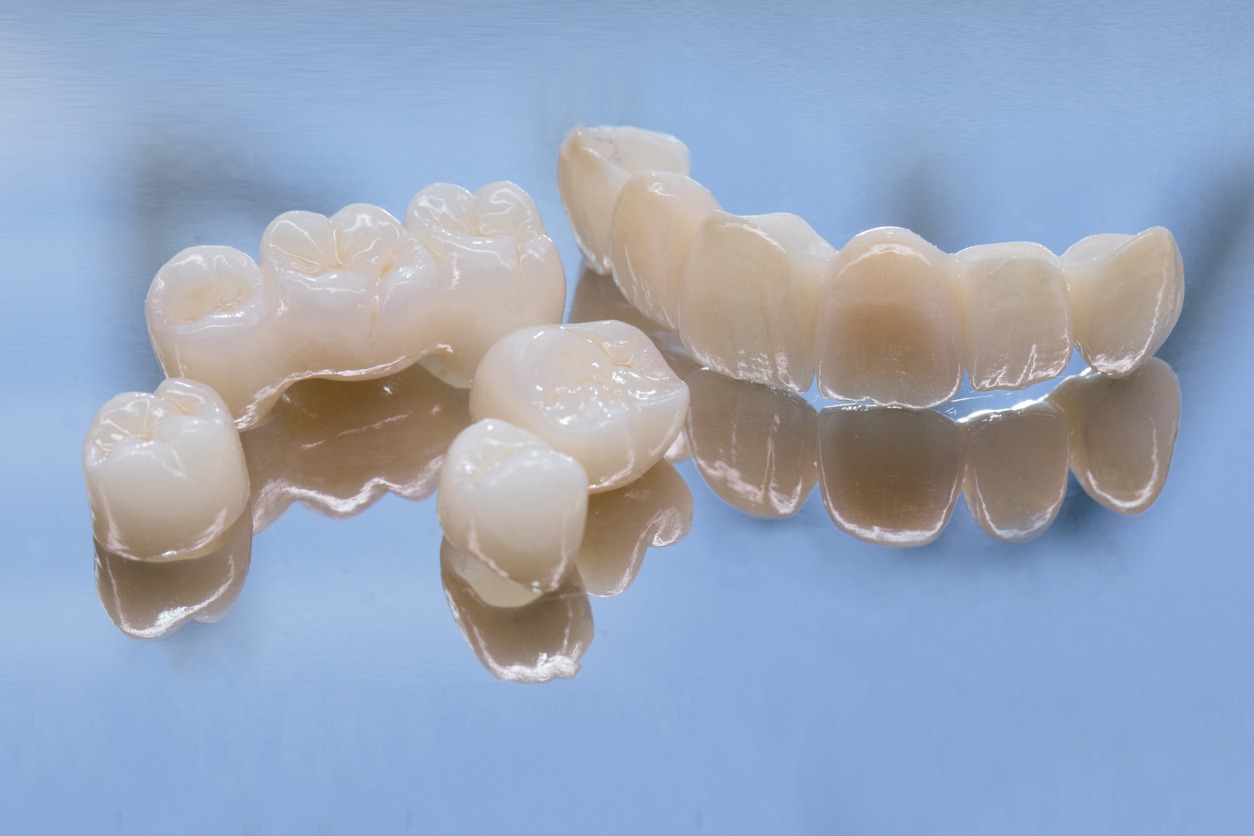
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal crowns, commonly known as PFMs, are a type of dental crown that combines the strength of metal with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain. These crowns consist of a metal base or core that is fused with a layer of porcelain. The metal provides durability and strength, while the porcelain layer offers a natural tooth-like appearance.
The Benefits of PFMs
These crowns provide a unique combination of strength, aesthetics, and versatility, making them suitable for a wide range of dental restoration needs. Here are some expanded benefits:
1. Durability and Strength
- Longevity: PFMs are known for their long-term durability. When properly maintained, they can last for many years, sometimes even decades.
- Resistance to Fracture: The metal foundation provides excellent resistance to fracture and wear, making PFMs ideal for restoring molars that endure heavy biting forces.
- Protection of Tooth Structure: By covering the entire tooth, PFMs protect against further decay and damage, preserving the remaining tooth structure.
2. Aesthetic Appeal
- Natural-Looking Appearance: The porcelain layer can be crafted to closely match the color and translucency of adjacent natural teeth, offering a more aesthetic appearance.
- Customizable Shape and Color: PFMs can be tailored to fit the shape and color of the patient’s existing teeth, ensuring a seamless blend with the natural dental arch.
- Improved Smile Aesthetics: For front teeth restorations, PFMs can be designed to enhance the overall appearance of a patient’s smile.
3. Versatility
- Suitable for Various Dental Issues: PFMs are not only used for crowns but also for bridges, implant abutments, and other restorative needs.
- Adaptable to Different Clinical Situations: They can be used in cases of severe tooth decay, root canal treatments, and for restoring teeth with significant structural damage.
4. Biocompatibility
- Low Allergy Risk: The metals used in PFMs are typically biocompatible, posing a low risk of allergic reactions.
- Tissue Compatibility: PFMs are generally well-tolerated by the surrounding gum and mouth tissues.
5. Functionality
- Effective Chewing Function: PFMs restore the tooth’s ability to chew effectively, distributing bite forces evenly and preventing further oral health issues.
- Speech Improvement: In cases where tooth loss affects speech, PFMs can help in restoring normal speech patterns.
6. Stability and Fit
- Secure Fit: PFMs are cemented onto the tooth, providing a secure and stable fit.
- Customized for Each Patient: Every PFM is custom-made to fit the specific contours of the patient’s tooth, ensuring comfort and functionality.
Considerations and Limitations
- Wear on Opposing Teeth: The porcelain part of PFM crowns can wear down opposing natural teeth more than metal or resin crowns.
- Aesthetic Limitations: In some cases, the metal underlying the porcelain can create a dark line near the gum line.
- Risk of Chipping: The porcelain layer, while strong, is more prone to chipping compared to all-metal crowns.
- Longevity: While durable, PFMs may not last as long as all-metal crowns due to the potential for porcelain chipping.
Technological Advancements in PFMs
Making the Right Choice
Whether a PFM crown is right for you depends on various factors, including the location of the tooth, aesthetic needs, and budget. It’s important to discuss these with your dentist, who can provide guidance based on your specific dental situation.
Conclusion
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal crowns have stood the test of time in dental restorations. Their combination of durability and aesthetic appeal makes them a viable option for many patients. As dental technology continues to evolve, PFMs remain a testament to the enduring quest for balancing function and aesthetics in dentistry.