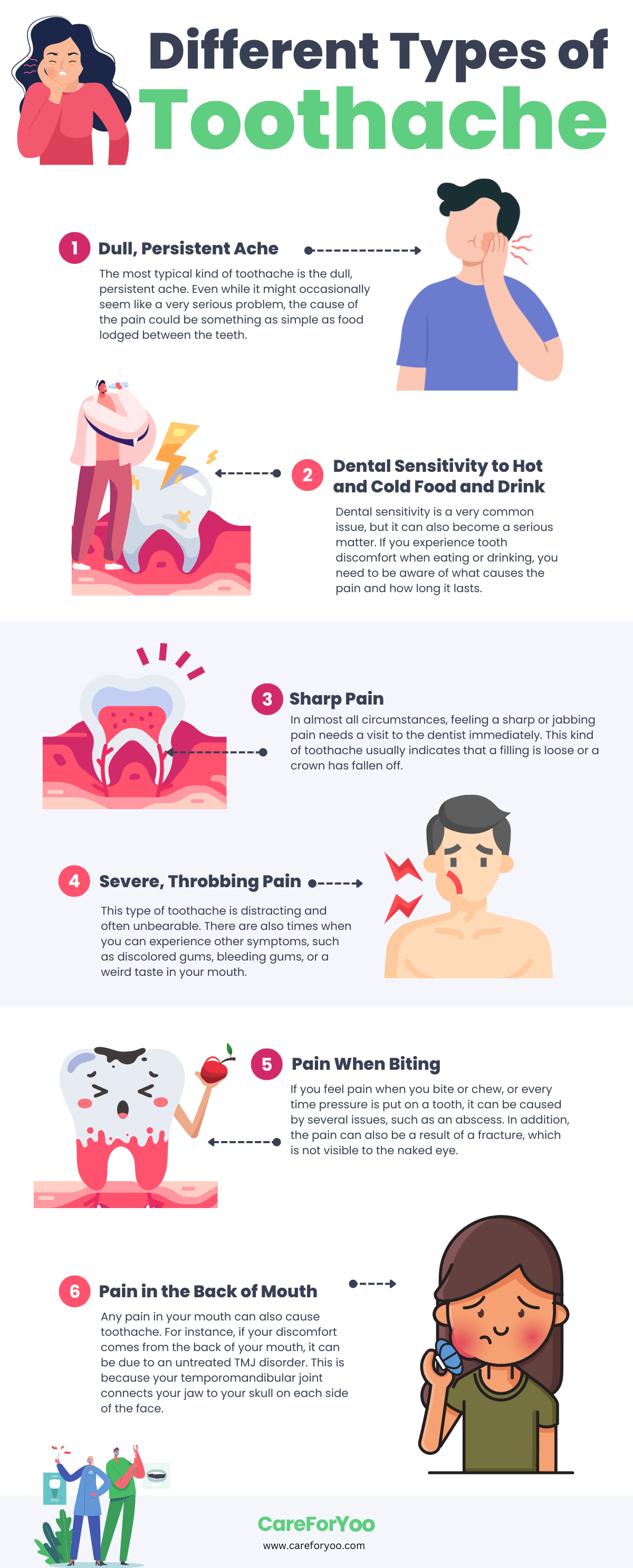
Toothaches are one of the most common medical complaints and can range from mild to severe in intensity. They can be a distracting and uncomfortable nuisance, disrupting your daily activities and activities. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, some toothaches can become increasingly uncomfortable and harder to manage over time.
When you experience a toothache, it is important to identify the cause in order to get the right toothache treatment and prevent further issues. But, with many different types of toothaches and their various causes, it can be difficult to know what’s causing yours.
For instance, a sensitivity toothache may require a different approach than a throbbing toothache. And, some types of toothaches may be caused by underlying conditions such as gum recession or enamel erosion. These need to be properly treated and managed in order to prevent further damage to your pearls.
This post focuses on the different types of toothaches and how to identify them. It also covers sensitivity toothaches, throbbing toothaches, sharp pain toothaches, and constant toothaches as well as some useful tips for managing and preventing each type.
Sensitivity Toothache
A sensitivity toothache is typically described as an ache or a burning feeling that comes on suddenly and is felt deep within the tooth when exposed to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances.
It is caused by damage or wear to the outermost layer of enamel on a tooth. This layer acts like a protective shell that keeps hot and cold temperatures from reaching the sensitive nerve inside. When this layer wears out, it exposes the nerve endings. When you eat or drink anything hot or cold, it causes a sharp pain in your teeth, which quickly subsides when the temperature returns to normal. This type of pain usually comes and goes quickly and is sharper than other types of toothaches.
Common Causes of Sensitivity Toothaches
Sensitivity toothaches are caused because of a damaged or weak enamel. This is the outermost layer of our teeth that protects the nerve inside our teeth from extreme temperatures.
Your enamel can become weak because of bad oral hygiene habits or habitual consumption of acidic foods and drinks. Enamel erosion can also be caused by conditions such as gum recession. In some cases dental procedures such as teeth whitening can also weaken enamel, leading to sensitivity. Aggressive brushing or underlying tooth decay can also cause you to suffer from sensitivity toothache.
Tips For Managing and Preventing Sensitivity Toothaches
If you are experiencing sensitivity toothaches, there are certain things you can do to manage and prevent them:
- First of all, limit your exposure to hot and cold foods by avoiding things like too much ice cream or coffee.
- Avoid acidic drinks and foods, like citrus fruits or soda, to prevent enamel erosion.
- Limit your intake of sugary snacks as much as possible.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to brush your teeth. A hard one can be harsh on an already weak enamel.
- Use a desensitizing toothpaste and mouthwash to help reduce pain and sensitivity.
- Brush your teeth after each meal, using gentle circular motions around sensitive areas. Be sure not to apply too much pressure on your already weak teeth.
- Brush your teeth twice a day and floss at least once daily.
- Finally, use a fluoride mouthwash twice daily to protect teeth from further damage.
- You can also have your dentist check for signs of tooth decay or infection, as this could also be making your teeth sensitive.
Throbbing Toothache
A throbbing toothache is characterized by a persistent pulsating ache accompanied by swelling, tenderness, and redness around the affected area. It feels like an intense pulsing sensation that comes and goes in waves, usually recurring at regular intervals for several minutes at a time before subsiding again briefly only to return again later.
This type of toothache is often caused by an underlying dental issue such as an abscess or an infection in the gums or teeth. You may feel sharp jolts of pain when biting down on food that quickly subside when you are not biting down anymore. The pain can also radiate outwards into the jaw and neck muscles when left untreated for an extended period of time.
Common Causes of Throbbing Toothaches
Throbbing toothaches are usually caused by an abscess or infection in the root of the affected tooth or the gum tissue surrounding it. Although, there may also be underlying decay involved or a traumatic injury to the face or jaw. Along with intense pain, you may also experience other symptoms such as swelling, redness, fever, or bad breath.
Tips For Managing and Preventing Throbbing Toothaches
It is important to seek prompt dental care if you’re experiencing a throbbing toothache. If left untreated, this type of toothache worsens over time and causes further damage to your teeth.
If you experience a throbbing toothache, be sure to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible in order to evaluate the cause of the pain. Once they have identified the cause of your toothache, they will determine the best treatment plan for your specific case. In some cases, antibiotics may be necessary if bacteria has spread into other areas of your mouth beyond just the affected area where the pain originated from.
After seeking medical attention, managing this type of toothache involves:
- Resting sufficiently
- Applying warm compresses to the affected area
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Avoiding triggers such as chewing hard foods or exposing teeth to extreme temperatures.
Preventing throbbing toothaches involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily and regular visits to the dentist for checkups and cleanings.
Sharp Pain Toothache
A sharp pain toothache is typically described as intense pain that comes on suddenly when exposed to pressure or temperature changes. The sudden bursts of intense pain are often followed by longer periods of less severe but still uncomfortable sensations that linger until the source of the discomfort is relieved.
This type of toothache is often caused by trauma or stress on one specific tooth, such as a cracked or chipped tooth, or an exposed nerve due to receding gums or periodontal disease. The sensation is usually sudden bursts of sharp pain when biting down on food that subsides shortly afterward but can gradually worsen over time if not addressed properly by your dentist.
Common Causes of Sharp Pain Toothaches
Sharp pain toothaches are usually caused by a cracked tooth or an exposed nerve. But they can also be brought about by sudden pressure or friction on the affected area such as clenching your teeth excessively while sleeping or grinding them during waking hours when you are stressed or anxious. You may also experience them due to cavity formation, trauma, dental abscesses, jaw joint problems (TMJ), and sinus infections.
Some underlying issues can also be causing the pain such as breaks, shifted teeth, or periodontal disease.
Tips For Managing and Preventing Sharp Pain Toothaches
If you experience sharp pain when biting down on something hard like ice cream or candy, it is important to avoid those items altogether so as not to aggravate your condition further. Continuing to consume such foods can cause more pain and discomfort later on down the line.
Follow these tips to manage sharp pain toothaches at home while awaiting your appointment with your dentist:
- Use warm salt water rinses followed by cold compresses
- Avoid chewing on the painful side
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen
- Take steps towards better oral hygiene such as brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled brush
- Soak cotton swabs in clove oil and apply directly onto painful spots
- Use fluoride-containing products like mouthwash or toothpaste which help protect against decay that could lead to nerve exposure
- You can consider using OTC oral numbing products specifically designed for dental pain relief
It is essential that you visit your dentist to manage your sharp pain toothache. In addition to prescribing pain meds, they may also suggest preventive care such as sealants on molars which helps safeguard them against cavities.
To prevent sharp pain toothache, make it a point to take good care of your teeth. Brush twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush, floss regularly, take a good diet, avoid overly sugary foods, and use fluoride-containing mouthwash to prevent tooth decay.
Constant Toothache
Constant toothaches cause gentle but lingering discomfort in one spot that doesn’t seem to go away even after taking over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. It is characterized as a persistent, ongoing dull ache that never seems to completely go away. No matter what you do.
This type of toothache tends to remain constant throughout most activities without becoming worse. Unless aggravated by some external factor, like physical stress or extreme temperatures. They can range from mild aches to intense throbbing depending on their cause.
Constant toothaches are usually brought about by underlying dental issues such as damaged fillings or crowns in addition to sinus infections (dental sinusitis). In this condition, the sinus pressure builds up around affected teeth due to disrupted air flow from colds or allergies.
Common Causes of Constant Toothaches
The most common causes of constant toothaches are damaged fillings that have left part of the sensitive inner layer exposed. But they can also be caused by
- Bacterial plaque build up leading to gum disease
- Grinding teeth
- Recent dental work
- Sinus infections
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder
- Poor oral hygiene
- Misaligned bite
- Dry mouth syndrome caused by certain medications like antacids and antidepressants
It is important to seek professional dental care if this type of painful sensation persists for more than two weeks. They may conduct investigations, such as scans of your mouth to diagnose the cause. Once the reason behind your pain is identified, appropriate treatment can begin depending on what issue is believed responsible for causing this persistent discomfort.
Tips For Managing and Preventing Constant Toothaches
To prevent constant toothaches from occurring, it is important to practice good dental hygiene including brushing twice daily, flossing once per day, drinking plenty of water and using mouthwash regularly. Additionally, avoiding sugary snacks and drinks between meals will help keep bacteria at the bay thus, decreasing the risk for developing this type of chronic pain.
At home, you can find relief from constant pains by using over-the-counter medications regularly. It is also important to avoid other contributing habits such as grinding, clenching, chewing hard candy, smoking, drinking alcohol etc.
You should also schedule regular checkups with your dentist for preventive care like cleanings and fillings. These visits help identify potential problems before they become more serious issues and need more involved treatments with greater associated cost/risks/time requirements etc.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, there are four main types of toothaches – sensitivity (burning feeling), throbbing (persistent ache), sharp pain (intense sudden pain) and constant (lingering discomfort) – each with their own causes, symptoms and treatments . It is important to identify which type best describes your current condition so that correct steps may be taken towards finding relief. Seek medical attention if your condition persists for more than two weeks despite your self-care measures. Note that some underlying conditions such as gum recession may require long-term management with continued visits with your dental professional.
Taking good care of your teeth is always important. To prevent future occurrences of these uncomfortable dental conditions, it’s helpful to establish and maintain good oral hygiene practices. This includes maintaining proper dental hygiene routines like brushing twice per day with soft bristles and flossing daily. Finally, employing preventive measures, such as avoiding overly acidic or sugary foods as well as refraining from grinding and clenching habits can also help you avoid toothaches. With proper care and regular visits everyone can enjoy comfortable smiles free from painful episodes.