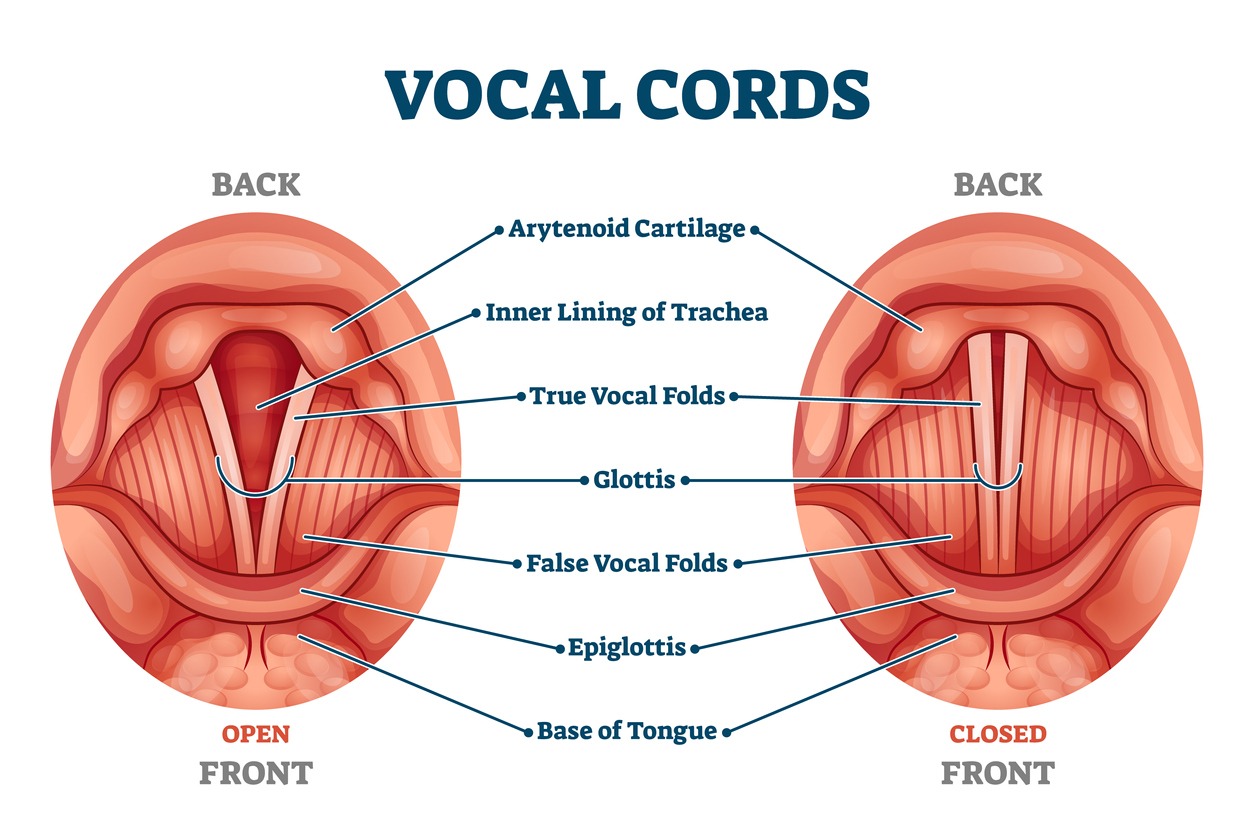
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, commonly known as the voice box. It typically results in a hoarse voice or the complete loss of the voice due to irritation or infection of the vocal cords. The condition can be short-term (acute) or long-lasting (chronic), and managing it requires understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Causes:
- Viral Infections: The most common cause of acute laryngitis.
- Vocal Strain: Yelling or overusing the voice can lead to inflammation.
- Bacterial Infections: Less common, but can cause more severe laryngitis.
- Allergies: Can contribute to chronic laryngitis.
- GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease can cause stomach acid to irritate the vocal cords.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Both can irritate the throat and lead to chronic laryngitis.
- Environmental Factors: Such as exposure to irritants like chemical fumes or allergens.
Symptoms:
- Hoarseness: A raspy, weak voice, or voice loss, is the most characteristic symptom of laryngitis.
- Throat Pain: There may be a raw feeling in the throat or pain, especially when swallowing.
- Dry Throat: A sensation of dryness in the throat is common.
- Dry Cough: Laryngitis can cause a persistent, non-productive cough.
- Tickling Sensation: Some people report a tickling feeling or irritation in the throat.
- Swollen Glands: You might feel tenderness or swelling in the area around your throat and neck.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Some individuals may have trouble swallowing due to the swelling and pain.
- Lost Voice: In more severe cases, laryngitis can lead to complete voice loss.
- Fever: Though not as common, some people may develop a low-grade fever with laryngitis, especially if it is caused by an infection.
- Breathing Difficulties: Rarely, laryngitis can cause breathing issues, particularly in children (croup).
These symptoms may vary in intensity, and not everyone will experience all of them. Most cases of acute laryngitis resolve on their own, but if symptoms persist for more than two weeks, worsen, or are accompanied by severe pain, high fever, or difficulty breathing, it’s important to seek medical attention. Chronic laryngitis or symptoms that frequently recur also warrant a consultation with a healthcare provider.
Acute Laryngitis: Short-term Voice Loss
Acute laryngitis typically resolves on its own within two weeks. The key to recovery is rest and self-care:
- Voice Rest: Speak as little as possible and avoid whispering, which can strain the voice more than speaking softly.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to keep the vocal cords moist. Warm tea with honey can be soothing.
- Humidify: Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air in your home.
- Avoid Irritants: Stay away from cigarette smoke and other irritants that can exacerbate the condition.
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Lozenges and gargles may provide temporary relief.
- Medical Attention: If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, worsen, or are accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing, or swallowing, seek medical advice.
Chronic Laryngitis: Long-term Management
Chronic laryngitis requires a comprehensive management plan, often involving lifestyle changes and medical treatment:
- Identify and Treat Underlying Causes: Conditions like allergies or GERD should be managed in coordination with healthcare providers.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce irritation.
- Voice Therapy: A speech-language pathologist can teach you how to use your voice more efficiently and prevent strain.
- Medication: In some cases, doctors may prescribe antibiotics (for bacterial infections), corticosteroids (to reduce inflammation), or other medications to treat underlying conditions.
- Surgery: In rare cases, such as when there are vocal cord lesions, surgery may be necessary.
Coping with the Loss of Voice
Losing your voice can be frustrating and impact daily life. Here are some tips for coping:
- Communicate Differently: Use written notes or text messages to communicate.
- Avoid Coughing and Clearing Your Throat: These actions can further irritate the vocal cords.
- Plan Ahead: If your work requires speaking, consider rescheduling speaking engagements or meetings until your voice returns.
- Patience: Be patient with your body as it heals, and give yourself time to recover fully.
Prevention
Conclusion
Laryngitis can be a disruptive condition, but most cases of acute laryngitis resolve with proper care and voice rest. Chronic laryngitis may require more intervention and lifestyle adjustments. Always consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your symptoms, especially if they persist or are severe. By taking care of your voice and being mindful of your throat’s health, you can minimize the impact of laryngitis and maintain effective communication in your daily life.